As climate change intensifies and population growth accelerates, the need for smarter, more efficient agricultural systems has never been more urgent. This article explores how AI technologies are already making an impact in Nigerian fields and examines the promising future applications that could revolutionise the country’s approach to food production.
Current Applications of AI in Nigerian Agriculture
Across Nigeria, innovative farmers and agritech startups are already harnessing the power of artificial intelligence to overcome longstanding agricultural challenges. These early adopters are demonstrating the practical benefits of technology-enhanced farming in the Nigerian context.
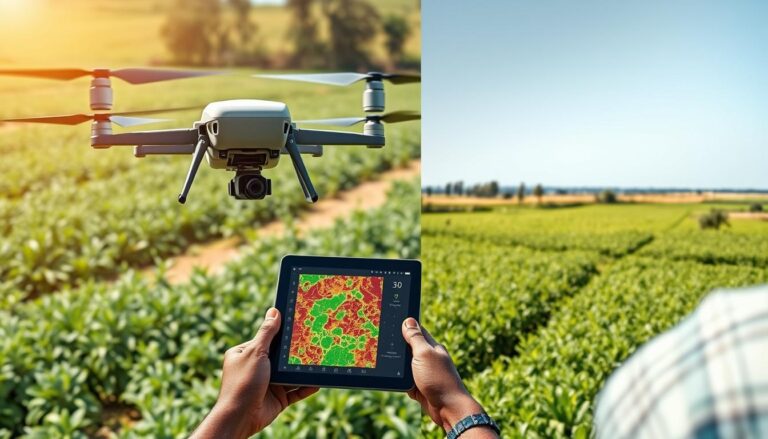
AI-powered drones provide Nigerian farmers with real-time crop health analysis.
Smart Crop Monitoring Systems
AI-powered drones and satellite imagery are revolutionising how Nigerian farmers monitor their crops. Companies like AirSmat are deploying these technologies to detect early signs of disease, nutrient deficiency, and pest invasion. This early detection system allows farmers to take timely action, significantly reducing crop losses that have traditionally plagued Nigerian agriculture.
“Nigerian farmers using mobile apps for crop management have increased production by up to 20% by addressing issues before they become widespread problems.”
Precision Farming Technologies
AI tools developed by Nigerian startups, such as Kitovu, analyse soil data, weather conditions, and historical crop performance to provide farmers with tailored recommendations. These insights help optimise planting times, fertiliser application, and irrigation schedules, reducing waste and improving productivity across Nigeria’s different regions.

Precision farming apps provide Nigerian farmers with actionable insights
Weather Prediction and Climate Intelligence
AI-driven platforms provide hyper-local weather forecasts that help Nigerian farmers plan planting and harvesting more accurately. These systems analyse historical weather patterns and current conditions to predict rainfall, temperature changes, and potential extreme weather events, reducing climate-related risks that have traditionally caused significant losses.
Automated Irrigation Systems
Some commercial farms in Nigeria have begun implementing AI-controlled irrigation systems that adjust water supply based on soil moisture and weather patterns. These innovative systems ensure crops receive optimal hydration while conserving Nigeria’s increasingly precious water resources.
Stay updated on AI Analysis and trends in Nigeria.
Join our newsletter to receive the latest updates on AI applications in Nigerian agriculture, including case studies, implementation guides, and funding opportunities.
Livestock Monitoring
AI-enabled sensors are helping Nigerian livestock farmers track animal health, detect diseases early, and optimise feeding schedules. These systems monitor vital signs and behaviour patterns, alerting farmers to potential health issues before they become serious, thereby improving livestock productivity and reducing losses.
Potential Future Applications of AI in Nigerian Agriculture
While current AI applications are already transforming Nigerian agriculture, the future holds even greater potential. As technology advances and becomes more accessible, several promising applications could further revolutionise farming practices across the country.
AI-powered market intelligence could transform how Nigerian farmers sell their produce.
AI-Powered Market Intelligence
Future AI systems could provide Nigerian farmers with real-time price data, demand forecasts, and supply trends. This market intelligence would enable farmers to sell at optimal prices and reduce exploitation by middlemen, a persistent problem in Nigeria’s agricultural value chain.
Predictive Yield Analytics
Advanced AI models could forecast crop yield at regional and national levels with unprecedented accuracy. These predictions would help Nigerian policymakers plan food supply and manage imports effectively, thereby strengthening the country’s food security.
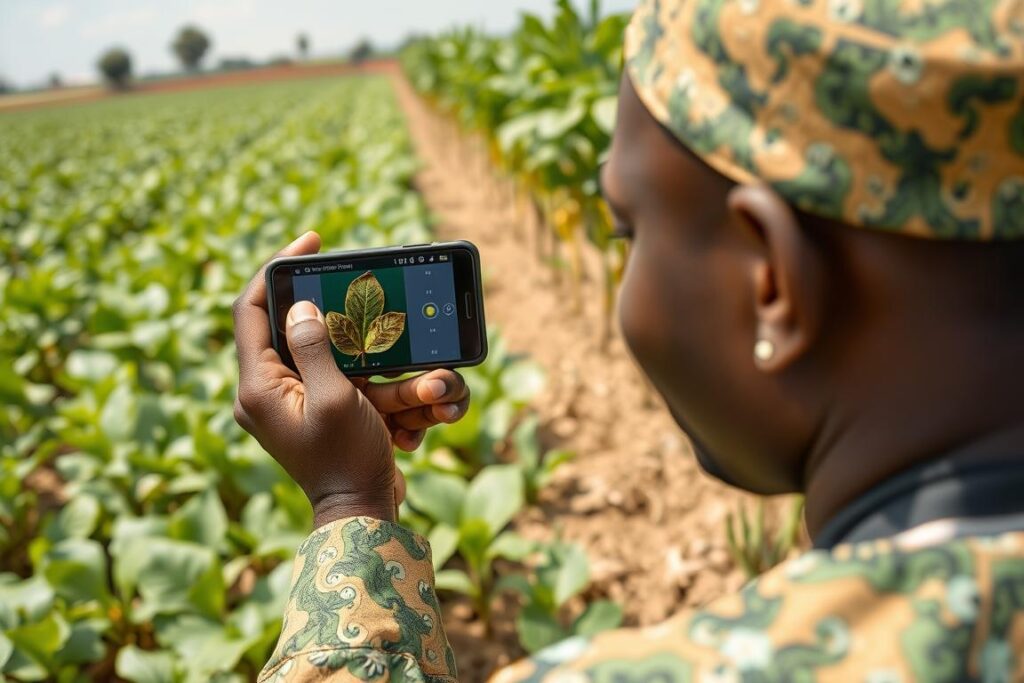

AI-powered disease detection apps could help farmers identify and treat crop issues instantly
Pest and Disease Detection Apps
Mobile apps using AI image recognition could enable Nigerian farmers to take photos of their crops and receive instant diagnoses and treatment recommendations. These accessible tools would democratise agricultural knowledge, bringing expert-level insights to smallholder farmers across the country.
Autonomous Farm Machinery
AI-driven tractors and harvesters could automate large-scale farming operations in Nigeria, addressing labour shortages and improving efficiency. While currently expensive, these technologies could become more accessible through cooperative ownership models and government subsidies.
AI-Optimised Seed Development
AI can support research to develop climate-resilient, high-yielding seed varieties tailored to Nigeria’s diverse agroecological zones. These tailored seed varieties could significantly boost productivity while requiring fewer inputs, making farming more sustainable and profitable.
AI Implementation Success Story: Jos Farmers
Farmers in Jos, Plateau State, have increased pepper production by 20% after implementing AI-driven greenhouse monitoring systems. These systems collect real-time data on temperature, humidity, soil moisture, and light levels, providing actionable insights for optimal growing conditions.
The technology has helped farmers reduce water usage by 30% while improving crop quality and market value.
Making AI a Practical Reality in Nigerian Agriculture
For AI to fulfil its transformative potential in Nigerian agriculture, strategic implementation approaches are essential. These strategies must address the unique challenges and opportunities within Nigeria’s agricultural landscape.
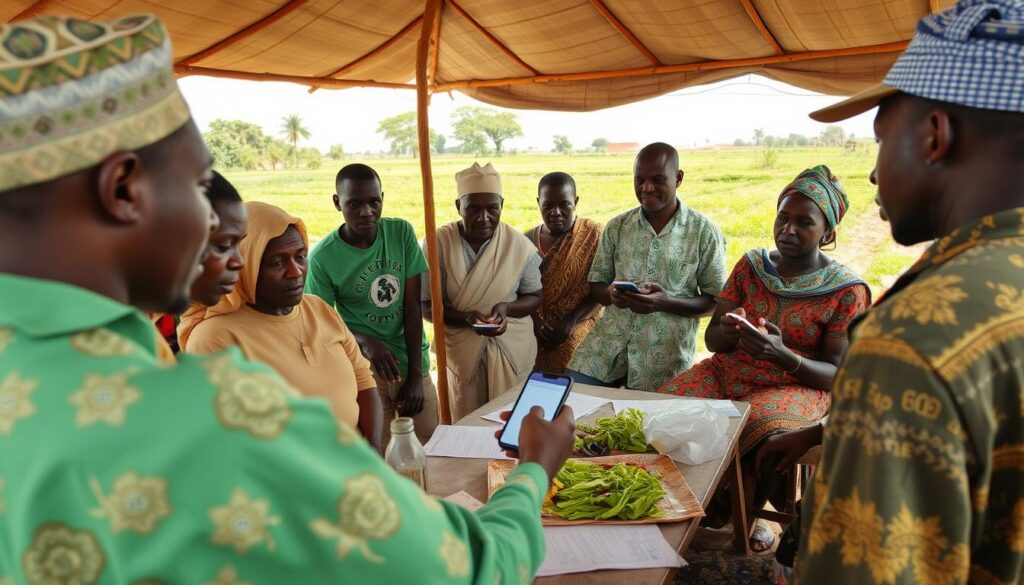

Training programs are essential for successful AI adoption among Nigerian farmers
Integration with Mobile Technology
AI tools must be embedded into mobile applications and USSD platforms to reach Nigeria’s smallholder farmers, many of whom lack smartphones or stable internet. Simple, text-based AI services can provide valuable insights even on basic mobile devices, ensuring technology benefits reach rural communities.
Public-Private Partnerships
Government collaboration with agritech startups, research institutions, and telecom companies can accelerate AI deployment across rural communities. Initiatives like the Nigeria Artificial Intelligence Research Scheme (NAIRS) demonstrate how these partnerships can support AI research and development in critical sectors like agriculture.
Localised Data Systems
Building Nigerian datasets on soil types, weather patterns, and crop behaviour is essential for accurate AI predictions. These localised data systems ensure AI solutions are relevant to Nigeria’s diverse agricultural contexts rather than relying on foreign data that may not apply to local conditions.
Farmer Education and Capacity Building
Training programs must be introduced to help Nigerian farmers understand and adopt AI solutions effectively. Programs like NITDA’s AI Developers Group are already working to train farmers on using AI tools and interpreting the insights they provide.
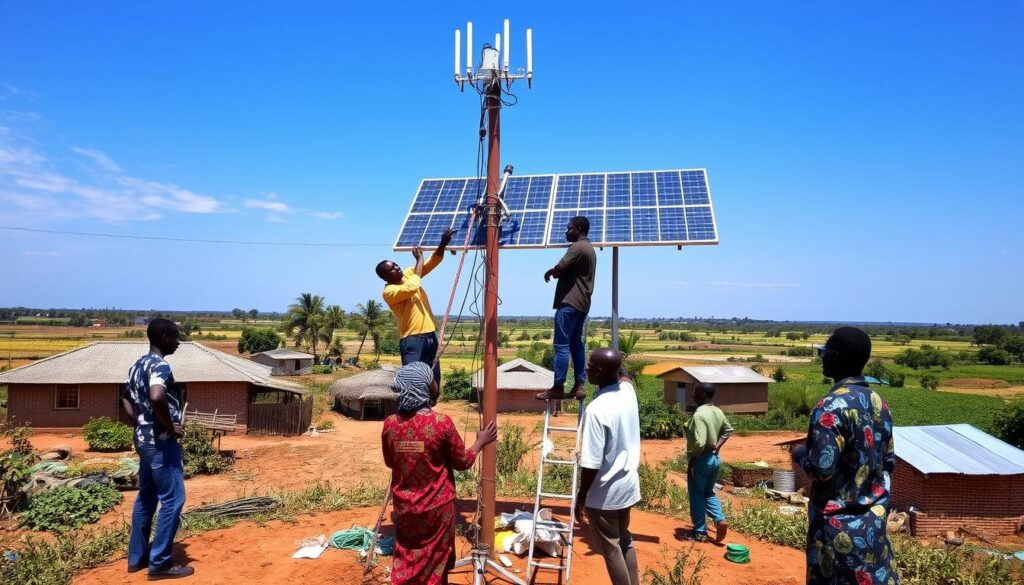

Infrastructure development is crucial for AI adoption in rural Nigerian communities
Infrastructure Development
Investment in rural connectivity, power supply, and cloud infrastructure will support seamless AI integration in Nigerian agriculture. Without reliable electricity and internet access, even the most promising AI solutions will struggle to gain traction in rural farming communities.
Stay updated on AI Analysis and trends in Nigeria
Join our newsletter to receive the latest updates on AI applications in Nigerian agriculture, including case studies, implementation guides, and funding opportunities.
Challenges Facing AI Adoption in Nigerian Agriculture
Despite its promising potential, AI adoption in Nigerian agriculture faces several significant challenges that must be addressed through coordinated efforts from various stakeholders.
Benefits of AI in Nigerian Agriculture
- Increased crop yields through precision farming
- Reduced resource waste (water, fertiliser, pesticides)
- Early detection of crop diseases and pests
- Better climate adaptation strategies
- Improved market access and pricing
Challenges to AI Adoption
- Limited digital infrastructure in rural areas
- High implementation costs for smallholder farmers
- Low digital literacy among farming communities
- Data scarcity and quality issues
- Regulatory gaps and policy uncertainties
Limited Digital Infrastructure
Poor internet penetration and inconsistent power supply hinder the deployment of AI technologies in rural Nigerian areas, where most agricultural activities take place. Without reliable connectivity, real-time data collection and analysis become challenging, limiting the effectiveness of AI solutions.

Digital literacy training is essential for successful AI adoption
High Implementation Costs
Advanced AI systems and smart equipment remain expensive for Nigeria’s small-scale farmers who often operate with limited capital. The initial investment required for sensors, drones, and other AI-enabled tools can be prohibitive without financial support mechanisms.
Low Digital Literacy
Many Nigerian farmers lack the technical knowledge needed to operate AI-based tools effectively. This knowledge gap can lead to underutilization of technology or incorrect implementation, reducing the potential benefits of AI solutions.

Building localised datasets is crucial for effective AI agricultural systems in Nigeria
Data Scarcity and Quality Issues
Inaccurate or insufficient agricultural data reduces AI system effectiveness in the Nigerian context. Without comprehensive, localised datasets on soil conditions, crop varieties, and climate patterns, AI algorithms may produce recommendations that aren’t optimised for local conditions.
Policy and Regulatory Gaps
Nigeria lacks strong policies specifically tailored to AI implementation in agriculture. This regulatory uncertainty can discourage investment and innovation in agricultural AI solutions, slowing the pace of adoption across the sector.
Resistance to Change
Traditional farming practices and scepticism towards new technology can slow acceptance of AI solutions among Nigerian farming communities. Overcoming this cultural resistance requires a demonstration of tangible benefits and respectful integration with existing knowledge systems.
| Challenge | Potential Solution | Key Stakeholders |
| Limited digital infrastructure | Rural connectivity initiatives, solar-powered AI systems | Government, telecom companies, energy providers |
| High implementation costs | Subsidies, cooperative ownership models, pay-as-you-go services | Government, financial institutions, agritech companies |
| Low digital literacy | Targeted training programs, simplified interfaces, and local tech champions | NGOs, extension services, and educational institutions |
| Data scarcity | Collaborative data collection initiatives, farmer incentives for data sharing | Research institutions, farmer cooperatives, agritech startups |
| Policy gaps | Development of an AI agricultural policy framework, regulatory sandboxes | Government agencies, policy experts, and agricultural associations |
The Way Forward: Bridging the Gap Between AI Potential and Reality
For AI to truly revolutionise Nigerian agriculture, stakeholders must focus on affordability, accessibility, and local relevance. Government incentives, agritech innovation hubs, and community-based training programs will play a vital role in bridging the gap between AI potential and practical reality.
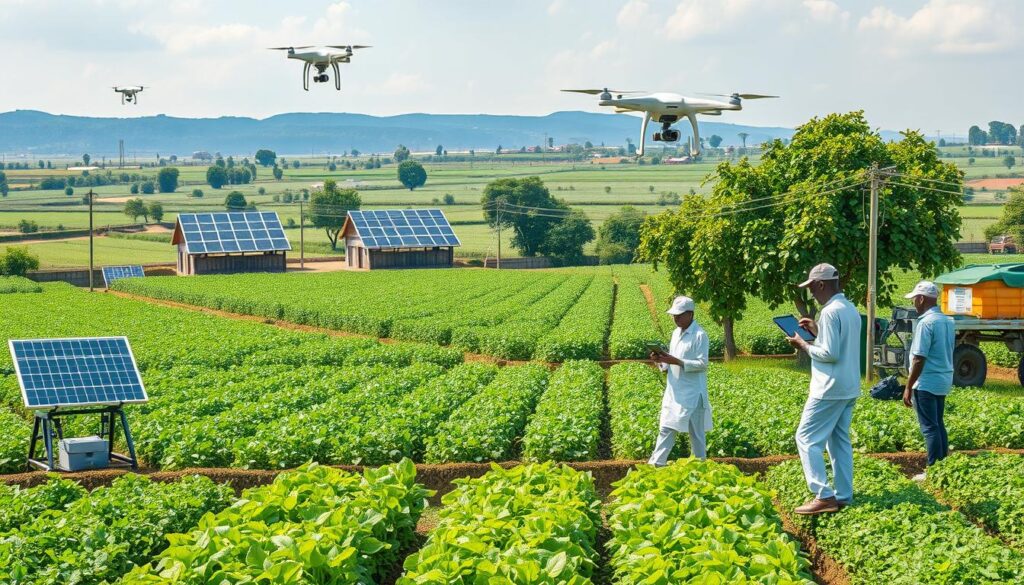

AI technologies can help transform Nigerian agriculture into a data-driven, sustainable sector.
By embracing AI, Nigeria can move from subsistence farming to a data-driven agricultural economy that enhances food security, supports export growth, and empowers rural communities. The transformation won’t happen overnight, but with strategic investments and collaborative efforts, AI can help unlock the immense potential of Nigerian agriculture.
As climate challenges intensify and population pressures grow, the adoption of AI in agriculture isn’t just an opportunity-it’s increasingly becoming a necessity for Nigeria’s sustainable development and food security future.
Stay updated on AI Analysis and trends in Nigeria.
Join our newsletter to receive the latest updates on AI applications in Nigerian agriculture, including case studies, implementation guides, and funding opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI in Nigerian Agriculture
How affordable are AI agricultural technologies for small-scale Nigerian farmers?
While some AI technologies require significant investment, many solutions are becoming increasingly affordable. Mobile-based applications, cooperative ownership models, and pay-as-you-go services are making AI more accessible to smallholder farmers. Government subsidies and NGO programs are also helping reduce costs for early adopters.
What kind of internet connectivity is needed for AI agricultural tools?
Connectivity requirements vary by solution. Some advanced systems require continuous high-speed internet, but many applications are designed for intermittent connectivity or can function offline with periodic synchronisation. USSD-based services can even deliver AI insights via basic feature phones without internet access.
How can AI help Nigerian farmers adapt to climate change?
AI provides several climate adaptation tools, including precise weather forecasting, drought-resistant crop recommendations, optimal planting time predictions, and water conservation techniques. These insights help farmers make informed decisions amid increasingly unpredictable weather patterns.
What role can the government play in promoting AI adoption in agriculture?
The government can accelerate AI adoption by developing infrastructure, implementing supportive policies, funding research, offering tax incentives for agritech companies, and subsidising farmers adopting new technologies. Creating regulatory frameworks that encourage innovation while protecting farmers’ interests is also crucial.

Senior Reporter/Editor
Bio: Ugochukwu is a freelance journalist and Editor at AIbase.ng, with a strong professional focus on investigative reporting. He holds a degree in Mass Communication and brings extensive experience in news gathering, reporting, and editorial writing. With over a decade of active engagement across diverse news outlets, he contributes in-depth analytical, practical, and expository articles exploring artificial intelligence and its real-world impact. His seasoned newsroom experience and well-established information networks provide AIbase.ng with credible, timely, and high-quality coverage of emerging AI developments.

