Over the past decade, artificial intelligence has shifted from academic research into everyday economic and organisational life. Early advances in machine learning reshaped search engines, recommendation systems, and digital advertising. More recently, large language models have captured global attention for their ability to write, summarise, translate, and reason in natural language.
As public enthusiasm accelerated, a clear divide emerged between consumer-facing AI tools and the practical requirements of large organisations. Enterprises need systems that are dependable, controllable, and aligned with internal governance frameworks. They must also operate effectively in specialised domains such as law, finance, healthcare, and public administration, where errors carry material consequences.
This growing mismatch has driven the rise of a new class of AI providers. Rather than pursuing viral adoption or consumer interfaces, these companies focus on infrastructure-grade language intelligence designed for long-term organisational use. One of the most prominent names in this category is Cohere. Instead of presenting itself as a chatbot brand, Cohere has concentrated on building enterprise language models that integrate quietly but deeply into business systems. Understanding Cohere offers a useful lens for examining how language models are evolving beyond novelty into durable organisational tools.
What Is Cohere AI?
Cohere is an artificial intelligence company specialising in large language models built specifically for enterprise environments. Founded in 2019 by researchers with extensive experience in natural language processing, the company focuses on enabling organisations to embed advanced language understanding directly into products, workflows, and data systems.
At its core, Cohere develops foundation models capable of tasks such as text generation, summarisation, semantic search, classification, and information retrieval. These models are delivered through application programming interfaces and private deployment options, allowing organisations to build tailored applications without training large models from scratch.
What distinguishes Cohere is not only the technical strength of its models but the design philosophy behind them. The company places strong emphasis on security, data control, and adaptability, reflecting the regulatory, operational, and reputational constraints under which enterprises operate.
Understanding Enterprise Language Models
To understand Cohere’s role, it is important to clarify what enterprise language models mean in practice.
Large language models are neural networks trained on vast volumes of text to learn statistical patterns in language. Rather than storing facts in a traditional database, they generate responses by predicting the most likely next unit of text based on context. This enables them to perform a wide range of language tasks with considerable flexibility.
Enterprise language models build on this foundation while introducing additional priorities. They must integrate seamlessly with internal systems, respect access controls, and behave consistently in professional settings. In these environments, accuracy, traceability, and predictable behaviour are often more important than creativity or open-ended conversation.
Cohere’s models are designed with these requirements in mind and function as reliable components within broader information systems rather than standalone applications.
How Cohere’s Models Work in Practice
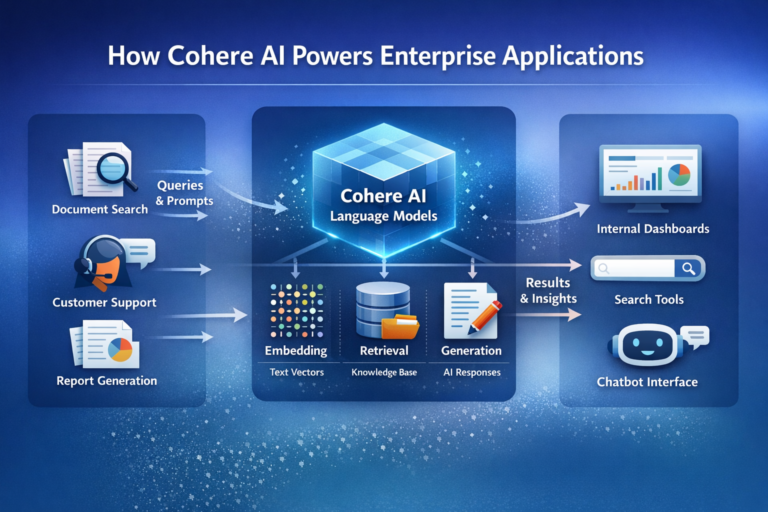
Cohere’s technology stack centres on pre-trained language models that can be adapted to organisational needs through fine-tuning and careful prompt design. In practice, enterprises tend to use these models in three principal ways.
First, for text generation and transformation. Organisations rely on Cohere to draft reports, summarise lengthy documents, rephrase content, or convert unstructured text into structured outputs. The emphasis is on consistency, accuracy, and domain relevance rather than expressive or conversational tone.
Second, for semantic understanding. Cohere’s embedding models transform text into numerical representations that capture meaning rather than surface keywords. These embeddings underpin semantic search, recommendation systems, and clustering tools that remain effective even when queries are phrased in unfamiliar or indirect ways.
Third, through retrieval-augmented workflows. By connecting language models to internal knowledge bases, organisations can build systems that answer questions using proprietary documents, policies, or archives, while retaining control over what information is accessed and how it is used.
Across all these applications, the models operate as probabilistic systems guided by organisational constraints, not as autonomous decision-makers.
Architecture and Deployment Options
One of Cohere’s defining characteristics is its flexible deployment approach. While many AI services rely exclusively on shared cloud infrastructure, Cohere offers options that better align with enterprise risk management requirements.
Organisations can access Cohere’s models through secure cloud APIs, benefiting from scalability and regular updates. For those with stricter confidentiality or data residency requirements, private cloud and virtual private cloud deployments are also available. In these environments, customer data remains isolated and is not used to retrain shared models.
This architectural flexibility enables enterprises to adopt advanced language models without weakening existing security or compliance postures. It also reflects a broader industry shift away from uniform AI platforms towards more configurable, enterprise-ready infrastructure.
Cohere’s Approach to Data Privacy and Governance
Data governance remains one of the most sensitive issues in enterprise AI adoption. Language models trained on large public datasets raise legitimate concerns around intellectual property, confidentiality, and regulatory compliance.
Cohere positions itself as a partner that respects organisational boundaries. Customer data processed through its systems is not reused for general model training unless explicitly agreed. Access controls, auditability, and usage monitoring are designed to integrate with established governance frameworks.
This approach has made Cohere particularly attractive to sectors where trust and accountability are critical. While no AI system is entirely without risk, the company’s emphasis on transparency and control addresses many of the concerns that slow enterprise adoption.
Comparing Cohere with Other AI Model Providers
The language model ecosystem includes consumer platforms, cloud hyperscalers, and open-source communities. Within this crowded landscape, Cohere occupies a distinct position.
Unlike consumer-oriented AI brands, Cohere does not prioritise end-user chat interfaces or mass-market adoption. Its technology operates largely behind the scenes, embedded in internal tools, enterprise software, and developer platforms.
Compared with cloud providers that tightly bundle AI into broader infrastructure offerings, Cohere positions itself as platform-neutral. Organisations can integrate their models without committing to a single cloud ecosystem.
Relative to open-source alternatives, Cohere offers managed performance, enterprise-grade support, and contractual assurances that many organisations consider essential. This balance between openness and reliability reflects a pragmatic understanding of enterprise priorities.
Key Capabilities: Why Enterprises Use Cohere
Enterprises adopt Cohere for its ability to deliver reliable, adaptable, and secure language intelligence. Its core capabilities include:
-
Enterprise-Grade Large Language Models – Designed for professional and organisational use, rather than consumer chatbots.
-
Semantic Search and Embeddings – Enables meaning-based document search, recommendation, and clustering beyond keyword matching.
-
Text Generation for Workflows – Drafts reports, summarises documents, rephrases content, and converts unstructured text into structured outputs.
-
Retrieval-Augmented Workflows (RAG) – Answers questions using internal knowledge bases while maintaining control over proprietary data.
-
Data Privacy and Control – Customer data is kept secure and not used for general model training unless explicitly authorised.
-
Flexible Deployment Options – Available via secure cloud APIs, private cloud, or virtual private cloud environments.
-
Platform-Neutral Integration – Works across cloud providers, avoiding vendor lock-in.
-
Enterprise Governance Features – Provides auditability, access controls, and usage monitoring to meet compliance requirements.
-
Support for Regulated Industries – Ensures predictable, traceable, and reliable outputs for high-trust sectors.
-
Behind-the-Scenes AI Infrastructure – Powers internal tools and software rather than public-facing applications.
This section highlights why Cohere is valued as a dependable, adaptable, and enterprise-ready language model platform.
Economic and Organisational Implications
The expansion of enterprise language models carries implications beyond individual companies. Within organisations, they are reshaping how knowledge work is performed. Routine, text-intensive tasks can be partially automated, allowing professionals to focus on judgment, strategy, and interpersonal responsibilities.
At a broader economic level, this shift could improve productivity in sectors that have historically resisted automation. Language models enable scaling certain cognitive functions without proportionally increasing headcount.
These gains, however, depend on disciplined implementation. Poorly governed systems can introduce errors, bias, or overreliance, undermining trust rather than enhancing it. Cohere’s enterprise-first approach reflects the understanding that lasting impact requires institutional alignment, not just technical capability.
Limitations and Ongoing Challenges
Despite their strengths, Cohere’s models share limitations common to all large language models. They can generate convincing but incorrect outputs, struggle with highly specialised or novel questions, and reflect biases present in their training data.
For enterprises, these limitations make safeguards essential. Human oversight, validation processes, and clear accountability structures remain critical. Language models are tools that support decision-making, not authorities that replace it.
Additional challenges include cost, integration complexity, and skills gaps. Successful deployment requires not only robust technical infrastructure but also organisational readiness and workforce understanding.
The Future Direction of Cohere and Enterprise AI
Cohere’s evolution reflects a broader shift in artificial intelligence away from spectacle towards dependable, specialised systems. As language models mature, competitive advantage is likely to depend less on model size and more on integration quality, governance, and domain alignment.
Future progress may involve closer integration between language models and structured data, improved interpretability, and more precise control over model behaviour. These developments will determine whether enterprise AI becomes a strategic foundation or remains a peripheral capability.
Cohere’s emphasis on collaboration suggests a future in which language models are shaped as much by institutional needs as by research benchmarks.
Closing…
Cohere marks a key stage in the evolution of language models, shifting the focus from consumer hype to enterprise practicality. By emphasising security, control, and adaptability, it serves as an infrastructure provider rather than a source of AI spectacle.
Its value lies in augmenting human intelligence, embedding language understanding into organisational systems, rather than making bold claims about artificial general intelligence. Cohere’s significance comes from making advanced language models usable, accountable, and sustainable within complex institutions.

Senior Reporter/Editor
Bio: Ugochukwu is a freelance journalist and Editor at AIbase.ng, with a strong professional focus on investigative reporting. He holds a degree in Mass Communication and brings extensive experience in news gathering, reporting, and editorial writing. With over a decade of active engagement across diverse news outlets, he contributes in-depth analytical, practical, and expository articles exploring artificial intelligence and its real-world impact. His seasoned newsroom experience and well-established information networks provide AIbase.ng with credible, timely, and high-quality coverage of emerging AI developments.