However, the path to AI-enhanced policing in Nigeria is neither straightforward nor without concerns. While the technology offers unprecedented capabilities to analyse crime patterns and respond to threats, experts warn that without proper legal frameworks and oversight, these same tools could lead to privacy violations, discrimination, or surveillance overreach. This article explores the emerging role of AI in Nigerian law enforcement, examining both its transformative potential and the critical safeguards needed for responsible implementation.
Crime Pattern and Hotspot Analysis: Predicting Criminal Activity
AI-powered crime mapping system is analysing historical data to identify patterns and hotspots across Nigerian cities.
One of the most promising applications of AI in Nigerian policing is predictive crime analysis. By processing years of historical crime data, AI algorithms can identify patterns that human analysts might miss, revealing when and where specific crimes are most likely to occur. This approach transforms policing from reactive to proactive by enabling more strategic resource allocation.
The Nigeria Police Force currently collects substantial crime data, but much of it remains underutilised due to limitations in manual analysis. AI systems can process this information at scale, identifying correlations between crime types, locations, timing, and environmental factors. For example, an AI system might detect that armed robberies in Lagos spike during specific hours in particular neighbourhoods, allowing commanders to deploy patrols more effectively.
In cities like Abuja and Port Harcourt, preliminary AI models are already being tested to map crime hotspots. These systems analyse factors such as previous incident reports, population density, economic indicators, and even infrastructure quality to generate heat maps showing high-risk areas. For resource-constrained police departments, this intelligence-led approach ensures officers are positioned where they can have the most significant impact.
“The 80/20 principle applies to crime—approximately 80% of crimes occur in 20% of locations. AI helps us identify that critical 20%, allowing more efficient deployment of our limited resources.”
Faster Emergency Response: AI-Powered Dispatch Systems
Emergency response times can mean the difference between life and death. In Nigeria’s congested urban centres, police vehicles often struggle with traffic and navigation challenges when responding to incidents. AI systems are now being developed to optimise these critical response operations.
Advanced AI dispatch systems can process multiple data streams simultaneously-traffic patterns, road closures, weather conditions, and vehicle locations—to calculate the fastest possible routes for emergency responders. In Lagos, where traffic congestion is notorious, such systems could significantly reduce response times by routing patrol vehicles through less congested streets.
Beyond routing, AI can also revolutionise how emergency calls are prioritised. Natural language processing (NLP) algorithms can analyse emergency calls in real-time, detecting key phrases, emotional distress signals, and urgency indicators. This allows dispatchers to quickly identify high-priority situations even when callers are panicked or unable to communicate clearly.
As social media becomes increasingly important for emergency reporting, AI tools can also monitor platforms for distress signals. During crises, these systems can filter through thousands of posts to identify genuine emergency reports, helping authorities respond to incidents that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Digital Evidence and CCTV Analysis: Enhancing Surveillance Capabilities

As Nigerian states expand their CCTV infrastructure, the volume of video footage has grown exponentially, creating both opportunities and challenges. Human operators cannot effectively monitor thousands of camera feeds simultaneously. Still, AI-powered computer vision systems can analyse this footage at scale, transforming passive surveillance into an active security tool.
Computer vision algorithms can be trained to detect specific objects (weapons, stolen vehicles), recognise unusual behaviours (loitering in sensitive areas, suspicious package abandonment), and even identify known persons of interest. In Lagos State, where CCTV deployment has increased significantly, AI systems could help security agencies move from reactive investigation to real-time threat detection.
These capabilities extend beyond live monitoring. For investigations, AI can rapidly search through days or weeks of archived footage to find specific vehicles, individuals, or incidents. This task would take human analysts weeks to complete manually. This acceleration in the processing of video evidence could significantly improve the Nigerian Police Force’s case clearance rates.
As body-worn cameras are gradually introduced to Nigerian law enforcement, AI will become even more crucial for managing this additional video evidence. Automated systems can tag, categorise, and analyse footage, making it searchable and usable for both investigations and officer accountability purposes.
AI Video Analytics Capabilities: Object detection, facial recognition (where legally permitted), behaviour analysis, crowd monitoring, automatic license plate recognition, and anomaly detection.
Cybercrime and Financial Fraud Investigations: Following Digital Trails
Nigeria faces significant challenges with cybercrime, including business email compromise (BEC) schemes, banking fraud, and cryptocurrency scams. Traditional investigation methods struggle to keep pace with these rapidly evolving digital threats, but AI offers powerful new capabilities for cybercrime units.
Machine learning algorithms can analyse thousands of financial transactions to identify suspicious patterns that might indicate fraud. These systems can detect anomalies that are invisible to human analysts, such as complex networks of accounts designed to obscure money laundering. For agencies like the Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC), such tools could dramatically improve their ability to identify and disrupt financial crimes.
In malware investigations, AI systems can analyse code to identify similarities with known attack patterns, helping investigators link different criminal operations. Natural language processing can also scan dark web forums and messaging platforms for relevant intelligence on planned attacks or the trading of stolen data.
As cryptocurrency adoption grows in Nigeria, AI tools are becoming essential for tracking illicit transactions. While blockchain transactions are pseudonymous, machine learning algorithms can analyse transaction patterns to identify suspicious wallet clusters and help investigators follow the money trail in ransomware or fraud cases.
Search and Rescue Operations: Finding Missing Persons
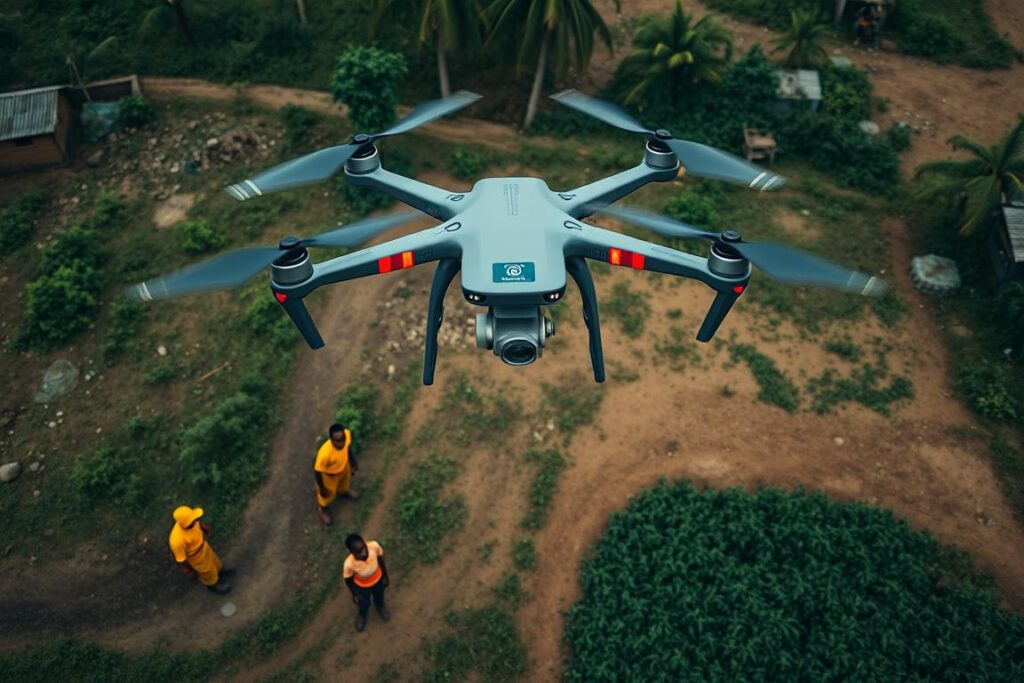

Kidnapping and missing person cases remain serious concerns across Nigeria. Vast search areas and limited manpower often hamper traditional search methods, but AI-enhanced technologies are creating new possibilities for these critical operations.
AI-powered drones equipped with thermal imaging and computer vision can survey large areas much faster than ground teams. These systems can be trained to distinguish between humans and animals, or to identify signs of vegetation disturbance that might indicate recent activity. In rural areas where kidnapping is prevalent, such aerial surveillance capabilities could significantly improve search efficiency.
For cases involving vehicles, AI can analyse CCTV footage from across a city to track a car’s movement, automatically identifying the exact vehicle across multiple cameras to reconstruct its route. This capability is particularly valuable in kidnapping investigations where rapid response is essential.
Facial recognition technology, when used with appropriate legal safeguards, can also assist in locating missing persons by scanning camera feeds for matches against a missing person’s photo. While privacy concerns must be carefully balanced, these technologies offer new hope for families of disappeared persons.
“In missing person cases, the first 48 hours are critical. AI systems can help us cover more ground faster, potentially making the difference between a successful rescue and a tragedy.”
Traffic Enforcement and Road Safety: AI on Nigerian Roads

Nigeria’s roads are among the most dangerous in Africa, with the Federal Road Safety Corps (FRSC) reporting thousands of fatalities annually. AI technologies offer new approaches to both enforcement and accident prevention that could significantly improve road safety.
Automated traffic monitoring systems using computer vision can detect various violations, such as speeding, dangerous driving, and illegal lane usage, without requiring an officer to be physically present. These systems can process video feeds from existing traffic cameras to identify infractions and generate evidence for enforcement actions.
Beyond enforcement, AI can optimise traffic flow through intelligent traffic management. By analysing real-time data from sensors and cameras, these systems can adjust traffic signal timing to reduce congestion and prevent the conditions that often lead to accidents. In cities like Lagos and Abuja, where traffic congestion causes significant economic losses, such systems could improve both safety and mobility.
AI can also identify accident-prone locations by analysing historical crash data alongside road conditions, weather patterns, and traffic volumes. This intelligence allows the FRSC and other agencies to implement targeted safety improvements at high-risk locations before accidents occur.
Deepfake and Media Verification: Combating Misinformation
In an era of sophisticated digital manipulation, deepfakes and other forms of synthetic media pose growing threats to public safety and election integrity in Nigeria. AI technologies are now being developed to detect these manipulations and verify the authenticity of digital content.
Deepfake detection algorithms analyse videos for subtle inconsistencies that indicate manipulation, such as unnatural blinking patterns, lighting inconsistencies, or facial movements that don’t match natural human expressions. These tools are particularly important during election periods when manipulated videos of political figures could trigger violence or unrest.
Audio forensics AI can similarly detect synthetic voice recordings by identifying the statistical patterns that differentiate AI-generated speech from authentic human recordings. For Nigerian security agencies investigating cases of fraud or extortion involving voice impersonation, these tools provide crucial verification capabilities.
Beyond detecting fakes, AI systems can also verify the authenticity of legitimate media by analysing metadata, checking for signs of tampering, and comparing content against known authentic sources. This verification capability is essential for security agencies to establish the reliability of digital evidence in investigations.
Officer Training and Simulation: Building Better Police Skills
Effective policing requires more than just technology-it demands well-trained officers with strong decision-making skills. AI-powered simulation systems are revolutionising how Nigerian law enforcement personnel are trained, particularly for high-stress scenarios that are difficult to replicate in traditional training environments.
Virtual reality (VR) training platforms enhanced with AI can create realistic scenarios that adapt based on an officer’s decisions and actions. These systems can simulate complex situations—hostage negotiations, armed confrontations, or crowd control incidents—allowing officers to practice critical skills in a safe environment before facing similar challenges in the field.
What makes these systems particularly valuable is their ability to provide personalised feedback. AI can analyse an officer’s performance, identifying areas for improvement in their decision-making, de-escalation techniques, or tactical responses. This data-driven approach ensures training addresses each officer’s specific development needs.
For the Nigerian Police Force, which has faced criticism for excessive use of force, these training systems offer a path to improve officers’ judgment in high-pressure situations. By repeatedly practising de-escalation techniques in realistic simulations, officers can develop the muscle memory and decision-making skills needed to resolve confrontations peacefully.
Stay updated on AI Analysis and trends in Nigeria.
Join our newsletter to receive the latest updates, news and analysis like this.
International Examples: Learning from Global AI Policing Initiatives
Nigeria can draw valuable lessons from countries that have already implemented AI in their law enforcement operations. These international examples provide both inspiration and cautionary tales as Nigeria develops its own approach to AI-enhanced policing.
United Kingdom: Real-Time CCTV Analysis
Police forces in London and Manchester use AI-assisted CCTV analysis to detect abandoned objects, identify unusual crowd movements, and spot potential safety risks during significant events. Rather than targeting individuals, these systems provide situational awareness alerts that help officers respond more effectively to emerging threats. The UK’s approach of combining technology with clear operational guidelines offers a model for balancing security benefits with privacy considerations.
United States: Gunshot Detection Systems
Cities like Chicago and New York use AI-powered acoustic sensors that can detect gunfire, pinpoint its location, and dispatch officers immediately. These systems have significantly reduced response times during firearm incidents, potentially saving lives through faster medical intervention. For Nigerian cities facing armed criminal activity, similar technology could provide valuable early warning capabilities.
Singapore: Automated Traffic Enforcement
Singapore uses AI-enabled road cameras to detect speeding, identify unauthorised lane changes, and automatically issue violations. This system has contributed to Singapore’s reputation for disciplined traffic management and could offer insights for Nigerian cities struggling with traffic enforcement challenges.
Canada: AI-Assisted Cybercrime Units
Canadian police use machine learning tools to analyse large datasets of digital evidence, detect fraud networks, trace ransomware payments, and filter harmful online content. These capabilities have improved the efficiency of digital investigations and could be particularly relevant for Nigeria’s growing cybercrime challenges.
Australia: Disaster and Emergency Response
Australian emergency services use AI during wildfires and floods to predict hazard movement, route responders, and analyse public reports in real-time. Some state police agencies integrate this information during large-scale evacuations, demonstrating how AI can support coordinated emergency responses.
South Korea: Predictive Traffic and Public Safety Systems
South Korean police use AI to predict crowd surges, optimise road-safety patrols, and monitor traffic congestion in major cities. These systems support city-level public safety management and could be adapted to help Nigerian authorities manage large public gatherings more safely.
Essential Safeguards: Ensuring Responsible AI Implementation
While AI offers powerful capabilities for Nigerian law enforcement, these technologies must be implemented with robust safeguards to prevent misuse and protect civil liberties. Without proper governance, AI systems risk reinforcing existing biases, enabling unauthorised surveillance, or undermining public trust.
Benefits of AI in Policing
- Enhanced crime prevention through predictive analytics
- More efficient resource allocation for police departments
- Faster emergency response times
- Improved investigation capabilities for complex crimes
- Better traffic management and road safety
- Enhanced officer training and decision-making
Risks Without Proper Safeguards
- Potential for algorithmic bias and discrimination
- Privacy violations through excessive surveillance
- Lack of transparency in automated decision-making
- Overreliance on technology at the expense of community policing
- Data security vulnerabilities
- Erosion of public trust in law enforcement
To implement AI responsibly, Nigeria needs a comprehensive governance framework that includes several key elements:
Legal and Regulatory Foundation
Nigeria currently lacks specific legislation governing the use of AI in law enforcement. Developing clear legal frameworks that define permitted uses, required safeguards, and accountability mechanisms is essential. These regulations should align with Nigeria’s existing data protection regulations while addressing the unique challenges of AI in policing contexts.
Oversight and Accountability
Independent oversight bodies comprising legal experts, technology specialists, civil society representatives, and law enforcement professionals should review and authorise AI deployments. Regular audits of AI systems can ensure they operate as intended and don’t produce discriminatory outcomes.
Transparency and Explainability
Law enforcement agencies should maintain transparency about which AI systems they deploy and how these systems inform decisions. When AI contributes to significant actions—such as arrests or resource allocation—the logic behind these recommendations should be explainable to oversight bodies and, when appropriate, to affected individuals.
Human Oversight
AI should support human decision-makers rather than replace them. Critical decisions-particularly those affecting individual rights-should always include meaningful human review rather than being fully automated. This “human in the loop” approach ensures accountability while leveraging AI’s analytical capabilities.
Warning: Implementing AI policing technologies without proper safeguards risks undermining public trust and potentially violating constitutional rights. Technology adoption must be balanced with strong governance and oversight mechanisms.
Implementation Challenges: Practical Barriers to AI Adoption
Beyond governance concerns, Nigeria faces several practical challenges in implementing AI for law enforcement. Addressing these barriers requires strategic investment and capacity building across multiple dimensions.
Infrastructure Limitations
Many AI systems require reliable electricity, high-speed internet connectivity, and substantial computing resources. In Nigeria, where power outages remain common and internet access is inconsistent in many areas, deploying advanced AI solutions presents significant infrastructure challenges. Investments in reliable power systems and connectivity are prerequisites for effective AI implementation.
Data Quality and Availability
AI systems are only as good as the data they’re trained on. Nigeria’s law enforcement agencies often struggle with fragmented, incomplete, or paper-based records that must be digitised and standardised before they can support AI applications. Developing comprehensive, high-quality datasets is a necessary foundation for effective AI systems.
Technical Expertise
Successfully implementing and maintaining AI systems requires specialised technical knowledge. Nigeria currently faces a shortage of AI experts, data scientists, and technical specialists within law enforcement agencies. Building this capacity through training programs and partnerships with academic institutions is essential for sustainable AI adoption.
Cost Constraints
Advanced AI systems can be expensive to develop, deploy, and maintain. With limited budgets, Nigerian law enforcement agencies must carefully prioritise investments and consider phased implementation approaches that deliver value while managing costs. Public-private partnerships may offer alternative funding models for some applications.
How can Nigeria address the infrastructure challenges for AI implementation?
Nigeria can adopt a phased approach, starting with AI applications that have lower infrastructure requirements or implementing solutions in urban centres with more reliable infrastructure first. Investments in solar power and other alternative energy sources can help address electricity challenges, while edge computing technologies that process data locally can reduce dependence on constant internet connectivity.
What role can international partnerships play in AI adoption?
International partnerships can provide technical expertise, funding support, and knowledge transfer to accelerate Nigeria’s AI capabilities. Collaborations with countries that have successfully implemented similar systems can help Nigeria avoid common pitfalls and adopt best practices. These partnerships should focus on building local capacity rather than creating dependency on foreign technology providers.
The Road Ahead: A Strategic Approach to AI in Nigerian Policing
Implementing AI in Nigerian policing requires a strategic, phased approach that balances technological innovation with appropriate safeguards. By developing a clear roadmap, Nigeria can harness AI’s benefits while mitigating risks and building public trust.
Phase 1: Foundation Building (1-2 Years)
The initial phase should focus on establishing the necessary foundations for successful AI implementation:
- Develop policy frameworks and governance structures for AI in law enforcement
- Invest in data digitisation, standardisation, and quality improvement
- Build technical capacity through training programs and partnerships
- Implement pilot projects focused on high-value, lower-risk applications
- Engage with communities to build understanding and address concerns
Phase 2: Capability Expansion (2-3 Years)
As foundations strengthen, Nigeria can expand AI capabilities in areas with proven value:
- Scale successful pilot projects to broader deployment
- Integrate AI systems with existing law enforcement processes and databases
- Develop specialised AI units within police departments and security agencies
- Implement more advanced applications with appropriate safeguards
- Establish robust evaluation frameworks to measure effectiveness
Phase 3: Advanced Integration (3-5 Years)
The final phase involves deeper integration of AI across policing operations:
- Implement advanced AI applications with strong governance mechanisms
- Develop cross-agency AI platforms to support coordinated security operations
- Build AI centres of excellence to drive continuous innovation
- Establish Nigeria as a regional leader in responsible AI for public safety
- Continuously refine governance frameworks based on operational experience
Stay updated on AI Analysis and trends in Nigeria.
Join our newsletter to receive the latest updates, news and analysis like this.
Balancing Innovation and Responsibility
AI has enormous potential to transform policing in Nigeria, offering new capabilities to address complex security challenges in an increasingly digital world. From predictive crime analysis to enhanced emergency response and sophisticated investigative tools, these technologies could significantly improve public safety outcomes nationwide.
However, the path to effective AI implementation is not merely technical-it requires careful attention to governance, ethics, and human rights. Without appropriate safeguards, even the most sophisticated AI systems risk undermining the very security they aim to enhance by eroding public trust or enabling abuses.
Nigeria stands at a critical juncture. By developing a thoughtful, strategic approach to AI in policing-one that combines technological innovation with strong governance frameworks and community engagement- the country can harness these powerful tools while protecting fundamental rights and liberties.
The future of policing in Nigeria will not be defined by technology alone, but by how that technology is governed, deployed, and integrated into broader security strategies. With responsible implementation, AI can become a valuable ally in building a safer, more secure Nigeria for all citizens.

Senior Reporter/Editor
Bio: Ugochukwu is a freelance journalist and Editor at AIbase.ng, with a strong professional focus on investigative reporting. He holds a degree in Mass Communication and brings extensive experience in news gathering, reporting, and editorial writing. With over a decade of active engagement across diverse news sources, he contributes in-depth analytical, practical, and expository articles that explore artificial intelligence and its real-world impact. His seasoned newsroom experience and well-established information networks provide AIbase.ng with credible, timely, and high-quality coverage of emerging AI developments.