Amidst these challenges, a promising solution is emerging. AI-powered telehealth-the integration of artificial intelligence with remote healthcare delivery-offers Nigeria an unprecedented opportunity to leapfrog traditional healthcare models. This digital transformation isn’t just a distant aspiration; it’s already taking root across the country, with pioneering platforms connecting patients to care regardless of location.
AI-powered telehealth platforms are making healthcare accessible to Nigerians regardless of location.
What Is AI-Powered Telehealth?
Telehealth itself isn’t new—it encompasses virtual consultations, remote monitoring, digital triage, and mobile health applications that connect patients with healthcare providers across distances. What makes today’s solutions revolutionary is the integration of artificial intelligence, which dramatically enhances these capabilities.
AI-powered telehealth goes beyond simple video calls with doctors. These systems employ sophisticated algorithms that can respond to patient symptoms, assist with preliminary diagnoses, predict health complications before they become severe, and automate administrative tasks like appointment scheduling and prescription management.
Core Components of AI-Powered Telehealth
- AI-driven symptom checkers that guide patients through structured assessments
- Diagnostic support tools that help healthcare providers analyse medical data.
- Predictive analytics that identify potential health risks before they escalate
- Natural language processing systems that understand patient queries
- Automated appointment and medication management systems
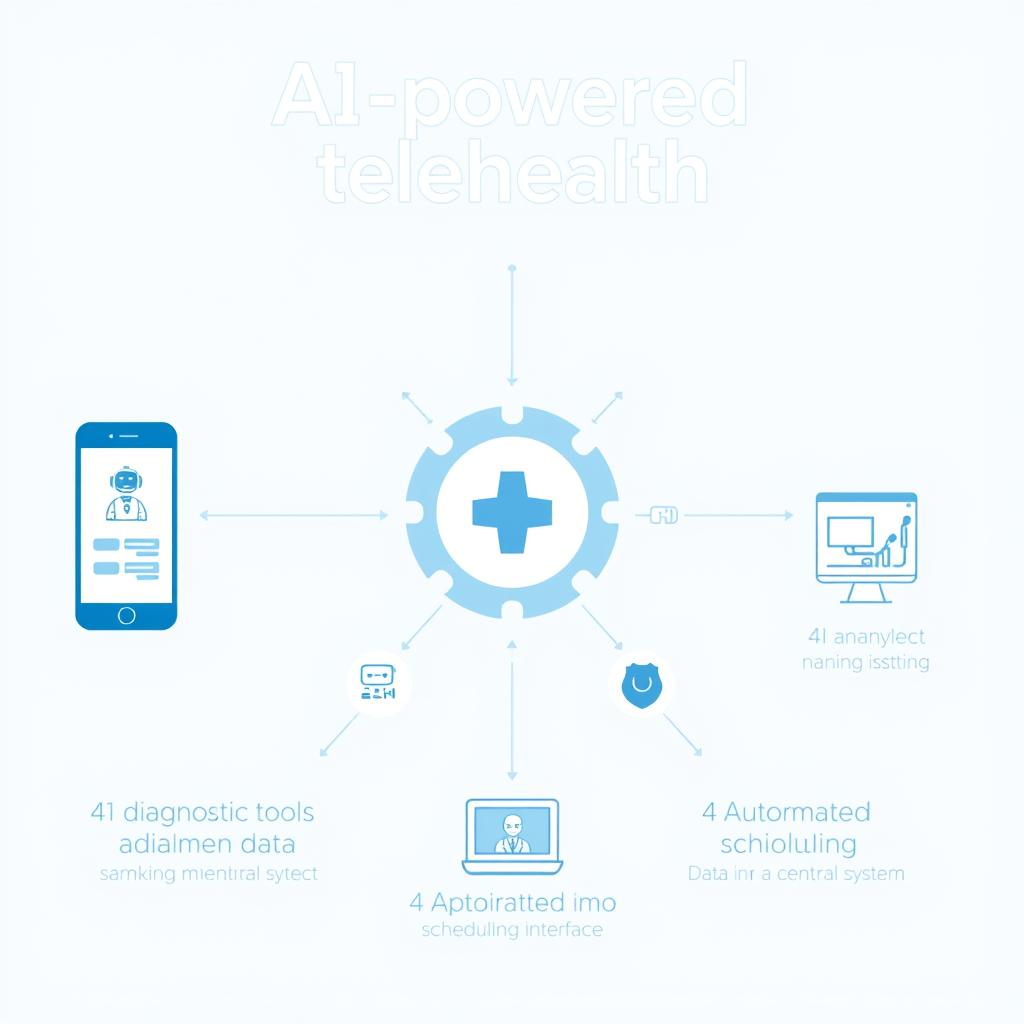
These systems can operate through various channels—from sophisticated web platforms to simple WhatsApp chatbots—making them adaptable to Nigeria’s diverse technological landscape. The flexibility allows AI-powered telehealth to reach Nigerians across different socioeconomic backgrounds and technological capabilities.
Why Nigeria Needs AI-Powered Telehealth
Nigeria’s healthcare challenges create a perfect environment for AI-powered telehealth solutions. The country’s severe doctor shortage means millions of Nigerians never receive adequate medical attention. Rural communities face particularly dire circumstances, with residents often travelling hours to reach the nearest qualified healthcare provider.
The burden of preventable and manageable diseases remains high, with conditions like malaria, hypertension, and diabetes causing significant mortality that could be reduced through consistent monitoring and early intervention. Meanwhile, the rising cost of private healthcare puts quality treatment beyond the reach of many Nigerians.
Enabling Factors for AI Telehealth in Nigeria
- Growing smartphone penetration (over 40% of the population)
- Expanding 4G coverage across major cities and towns
- Increasing digital literacy among younger generations
- Government initiatives supporting digital health innovation
- Rising acceptance of digital services in banking and commerce
Challenges to Address
- Inconsistent internet connectivity in rural areas
- Electricity supply limitations in many communities
- Digital literacy gaps, especially among older populations
- Data privacy and security concerns
- Need for stronger healthcare regulations and standards
Despite these challenges, Nigeria’s growing digital ecosystem provides fertile ground for AI-powered telehealth. With over 100 million internet users and widespread adoption of mobile technology, the infrastructure for digital health solutions is increasingly available to a significant portion of the population.
Stay Updated on Anything AI in Nigeria
Get our weekly newsletter with the latest developments in AI specifically for the Nigerian audience. Be the first to learn about new features and strategies.
Global Success Stories: Real-Life Examples of AI Telehealth in Action
Around the world, AI-powered telehealth is already demonstrating remarkable success in contexts similar to those in Nigeria. These examples provide valuable lessons and inspiration for Nigeria’s healthcare transformation.
India: AI Chatbots for Primary Healthcare

India’s healthcare challenges mirror Nigeria’s in many ways—large population, rural access issues, and doctor shortages. Companies like Practo and Apollo have deployed AI-driven symptom checkers that provide 24/7 triage and basic consultations to millions of Indians.
These platforms use natural language processing to understand patient concerns, provide initial guidance, and direct users to the appropriate level of care. The impact has been significant—reducing hospital queues by up to 30% in some regions and providing basic healthcare guidance to previously underserved rural communities.
Rwanda: Telemedicine for Rural Clinics
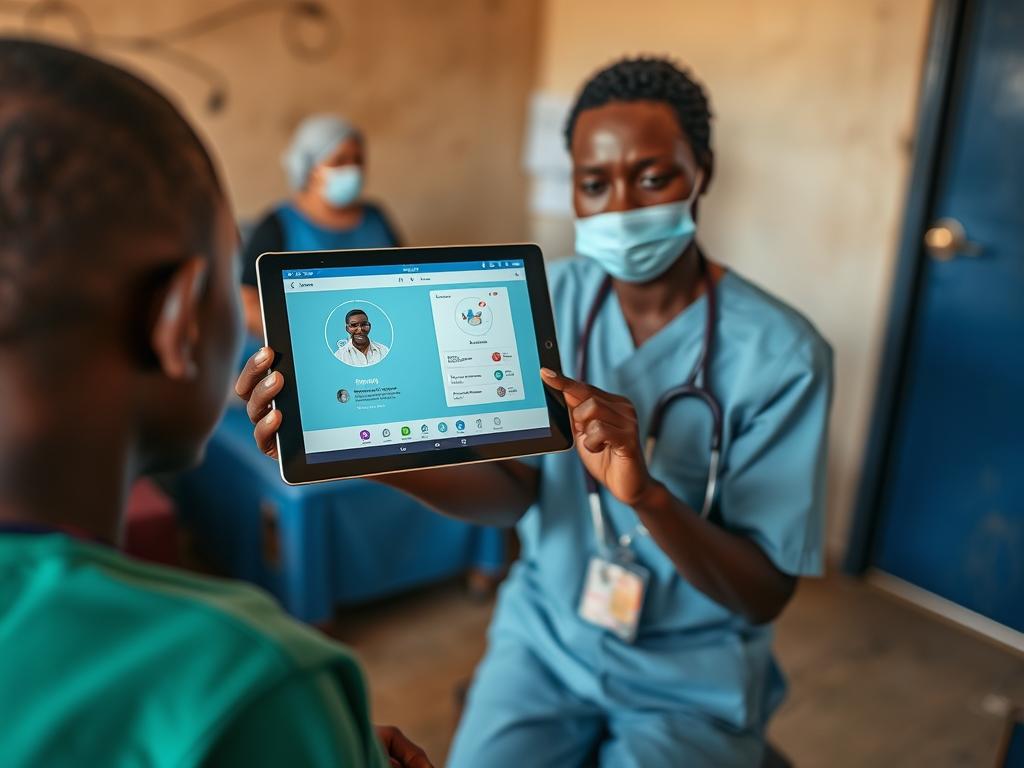
Rwanda has become a model for how low-income countries can successfully implement AI telehealth at scale. Their Babyl service, an AI-powered telehealth platform, has delivered over 2 million consultations to Rwandans, including those in remote villages far from hospitals.
The system uses AI-powered triage and messaging to efficiently connect patients with doctors. What makes Rwanda’s approach particularly relevant to Nigeria is its integration with the national health insurance scheme, making it accessible to citizens across socioeconomic levels.
United Kingdom: NHS Using AI for Initial Triage
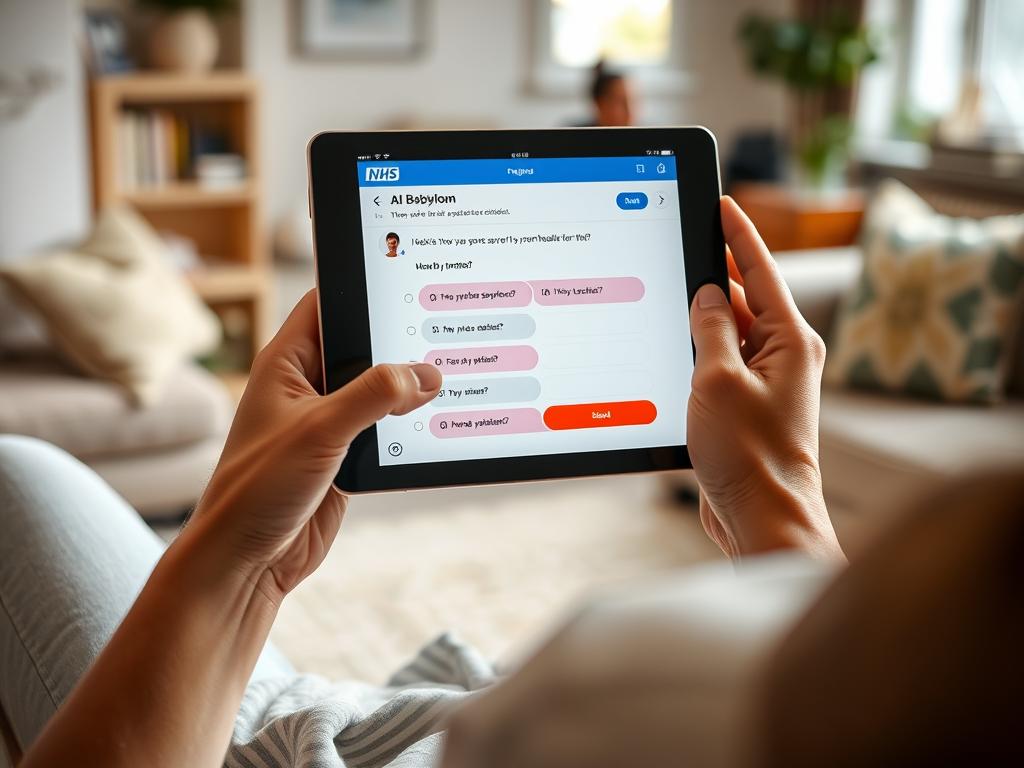
The UK’s National Health Service has integrated tools like Babylon AI for symptom checking and patient routing. These AI systems help manage high patient volumes by determining which cases require immediate in-person care and which can be handled through virtual consultations or self-care guidance.
The NHS experience demonstrates how AI can effectively support public healthcare systems. Their approach to clinical validation and safety protocols provides a valuable framework for Nigeria to consider when implementing similar solutions at scale.
Key Ways AI-Powered Telehealth Can Transform Nigeria’s Healthcare System
Drawing lessons from global examples and considering Nigeria’s specific context, AI-powered telehealth offers several transformative opportunities for the country’s healthcare system.
Improving Access for Remote & Underserved Communities
Nigeria’s geographical healthcare disparities could be significantly reduced through AI-powered telehealth. Rural communities that currently lack access to specialists could connect with doctors nationwide through their mobile phones. AI chatbots offering first-line medical advice can provide immediate guidance even in areas with limited connectivity.
The practical benefit is substantial—reducing the need for long-distance travel for medical care, which often prevents patients from seeking treatment until conditions become severe. For many Nigerians, this could mean the difference between early intervention and preventable complications.

Reducing Hospital Overcrowding
Nigeria’s urban hospitals are chronically overcrowded, with patients often waiting hours for consultations. AI triage tools can determine whether a patient needs in-person care or can be effectively treated remotely, significantly reducing unnecessary hospital visits.
By filtering patients who can be served through telehealth, hospitals can focus resources on emergencies and critical cases. Early implementations in Lagos have shown promising results, with some facilities reporting up to 25% reduction in non-emergency visits after introducing AI-powered pre-screening.
Better Diagnosis & Predictive Healthcare

AI algorithms can analyse symptoms, lab results, or medical images with remarkable accuracy. For conditions prevalent in Nigeria like malaria, tuberculosis, and hypertension, early detection through AI-assisted diagnosis could significantly improve outcomes.
Predictive healthcare—using AI to identify potential health issues before they become serious—represents a paradigm shift from reactive to preventive care. This approach is particularly valuable in Nigeria, where preventable complications from manageable conditions account for a significant portion of the healthcare burden.
Improved Chronic Disease Management
Chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and asthma require consistent monitoring and management. AI-powered remote monitoring tools can track patient metrics, provide medication reminders, and alert healthcare providers to concerning changes in patient status.
For Nigeria’s growing population of chronic disease patients, these tools offer a lifeline of continuous care without requiring frequent hospital visits. The economic impact is substantial—reducing complications that lead to hospitalizations while improving quality of life and productivity.
Lower Healthcare Costs
Perhaps most significantly for many Nigerians, AI-powered telehealth can dramatically reduce the cost of healthcare access. Virtual consultations typically cost 40-60% less than in-person visits, while AI-driven preliminary assessments can be provided at minimal or no cost to patients.
This cost reduction makes quality healthcare more accessible to low-income families who might otherwise avoid seeking care due to financial constraints. The economic benefits extend beyond individual patients to the healthcare system as a whole, enabling it to allocate resources more efficiently.
Challenges to Overcome in Nigeria
Despite its tremendous potential, implementing AI-powered telehealth in Nigeria faces several significant challenges that must be addressed thoughtfully.
| Challenge | Impact | Potential Solutions |
| Infrastructure Limitations | Inconsistent internet and electricity supply, especially in rural areas | Low-bandwidth applications, offline capabilities, solar-powered charging stations |
| Data Privacy Concerns | Patient hesitancy to share health data electronically | Robust encryption, clear consent protocols, transparent data usage policies |
| Digital Literacy Gaps | Difficulty using technology, especially among older populations | Simplified interfaces, community digital ambassadors, voice-controlled options |
| Regulatory Framework | Unclear standards for telehealth practice and AI implementation | Developing specific telehealth regulations and certification standards for AI health tools |
| Clinical Integration | Resistance from traditional healthcare providers | Training programs, phased implementation, demonstrating complementary benefits. |
Addressing these challenges requires collaboration among government agencies, private-sector innovators, healthcare providers, and communities. Success stories from countries like Rwanda and India demonstrate that with thoughtful implementation strategies, these obstacles can be overcome.
Recommendations for Nigeria
Drawing from global success stories and considering Nigeria’s unique context, several strategic recommendations emerge for effectively implementing AI-powered telehealth:

Cross-sector collaboration is essential for successful AI telehealth implementation in Nigeria.
Infrastructure Investment
Prioritise the development of digital health infrastructure, including reliable internet connectivity in healthcare facilities and community access points. Consider innovative solutions like satellite connectivity for remote areas and solar-powered charging stations to address electricity challenges.
Healthcare Worker Training
Develop comprehensive training programs for healthcare professionals on effectively utilising AI and telehealth tools. This should include both technical skills and guidance on integrating virtual care into clinical practice while maintaining quality standards.
Startup Ecosystem Support
Create incentives for telehealth startups through grants, tax benefits, and regulatory sandboxes that enable innovation while ensuring patient safety. Encourage the development of solutions designed explicitly for Nigeria’s unique healthcare challenges.
Data Protection Frameworks
Establish robust patient data protection regulations that balance innovation with privacy. Clear guidelines on data ownership, consent requirements, and security standards will build trust in digital health platforms.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Launch educational initiatives to familiarise Nigerians with the benefits and use of telehealth. Community-based demonstrations can help overcome resistance and build digital literacy among potential users.
Local AI Development
Support research and development of AI solutions specifically trained on Nigerian health data and contexts. Locally-developed AI will better address Nigeria-specific health challenges and cultural considerations.
These recommendations require coordinated effort across public and private sectors. The Nigerian Federal Ministry of Health, in collaboration with the Ministry of Communications and Digital Economy, could lead this initiative, bringing together healthcare providers, technology companies, and community representatives.
Conclusion
AI-powered telehealth represents a transformative opportunity for Nigeria’s healthcare system. By leveraging artificial intelligence and digital connectivity, Nigeria can address its most pressing healthcare challenges—from doctor shortages and rural access issues to the high burden of preventable diseases.
The global examples from Rwanda, India, and beyond demonstrate that these solutions can work effectively in contexts similar to Nigeria’s. With thoughtful implementation that addresses infrastructure limitations, regulatory needs, and cultural considerations, Nigeria can leapfrog traditional healthcare models to create a more accessible, efficient, and equitable system.
The journey toward AI-powered healthcare transformation will not be without challenges. However, the potential benefits—millions more Nigerians accessing quality care, reduced burden on hospitals, better management of chronic diseases, and ultimately, improved health outcomes across the population—make this a worthy and necessary pursuit.
As Nigeria continues its digital transformation journey, AI-powered telehealth stands as one of the most promising frontiers—not just for technological advancement, but for fundamental improvement in the health and well-being of millions of Nigerians.

Director
Bio: An (HND, BA, MBA, MSc) is a tech-savvy digital marketing professional, writing on artificial intelligence, digital tools, and emerging technologies. He holds an HND in Marketing, is a Chartered Marketer, earned an MBA in Marketing Management from LAUTECH, a BA in Marketing Management and Web Technologies from York St John University, and an MSc in Social Business and Marketing Management from the University of Salford, Manchester.
He has professional experience across sales, hospitality, healthcare, digital marketing, and business development, and has worked with Sheraton Hotels, A24 Group, and Kendal Nutricare. A skilled editor and web designer, He focuses on simplifying complex technologies and highlighting AI-driven opportunities for businesses and professionals.

