The Growing Landscape of AI in Nigeria’s Healthcare
Nigeria, alongside Ghana, leads Sub-Saharan Africa in developing innovative AI solutions for healthcare challenges. The private sector and academic institutions are driving this growth, creating locally relevant technologies that address Nigeria’s unique healthcare landscape. These solutions range from diagnostic tools to patient management systems, all designed to extend the reach of limited healthcare resources.
What makes this growth particularly significant is the focus on developing solutions that work within Nigeria’s infrastructure constraints while addressing critical healthcare needs. The result is an ecosystem of AI tools that are increasingly accessible to both urban and rural populations.
Current AI Implementations in Nigeria’s Health Sector
AI-Powered Chatbots for Public Health Outreach
One of the most successful implementations of AI in Nigeria’s healthcare system is AwaDoc’s WhatsApp chatbot. This innovative tool has transformed how Nigerians access reliable health information, particularly regarding immunisation. By early 2025, nearly 30,000 people had opted into the service, demonstrating its significant reach and impact.
Dr Chinonso Egemba, the Nigerian coordinator of AwaDoc, emphasises that the platform is “built by Africans, for Africans.” This local context ensures the information provided is culturally relevant and addresses the specific health concerns of Nigerian communities. The chatbot helps parents make informed vaccination decisions and provides critical information during disease outbreaks.
“Clafiya has been helpful to me. I didn’t know much about immunisation, so my husband suggested that we try Clafiya to get informed. Then diphtheria had just broken out, and I was terrified. Clafiya helped me see the need for immunisation, as well as make an informed decision.”
Telemedicine Platforms with AI Triage
Several telemedicine services in Nigeria now incorporate AI-powered triage systems that help route patients to appropriate care levels. These platforms use algorithmic assessments to determine urgency and connect patients with the right healthcare providers, optimising the use of limited specialist resources.
These AI-enhanced telemedicine services are particularly valuable in rural areas where access to specialists is limited. By providing preliminary assessments and routing patients appropriately, these platforms ensure efficient allocation of healthcare resources and improve access for underserved populations.
Diagnostic Assistance Tools
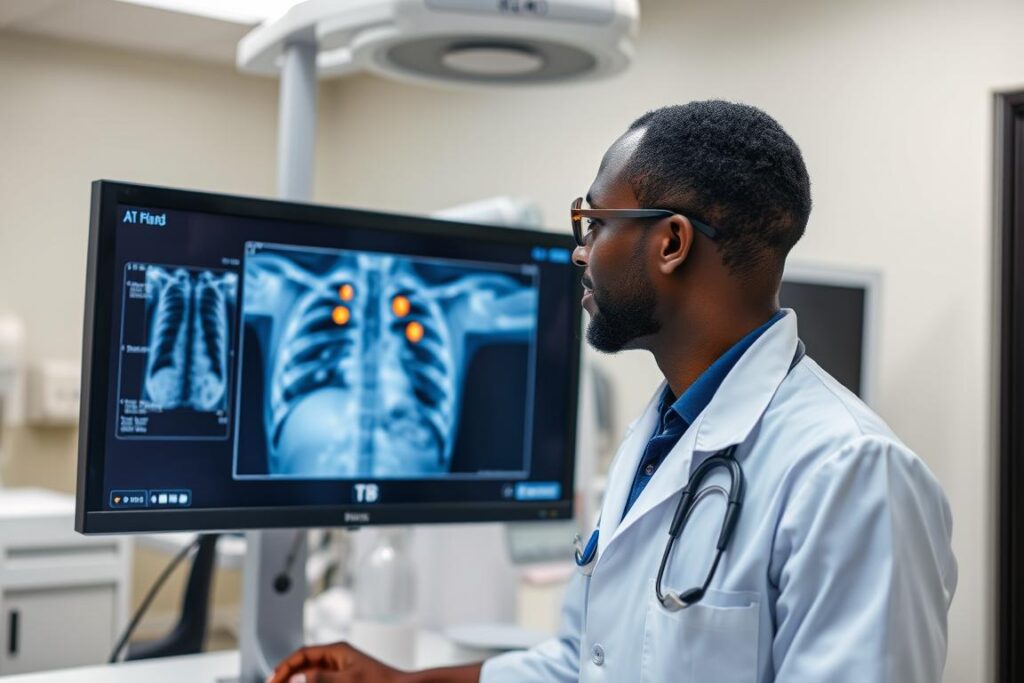
Private clinics and startups across Nigeria are piloting AI tools for diagnostic support, particularly in imaging analysis. These tools assist healthcare professionals in analysing chest X-rays for tuberculosis and other respiratory conditions, helping to address the shortage of radiologists in many parts of the country.
Laboratory data analytics powered by AI are also being implemented to improve the accuracy and speed of test results interpretation. These systems can flag abnormal results and suggest potential diagnoses, supporting healthcare providers in making more informed clinical decisions.
Health System Administration and Analytics
AI solutions are streamlining administrative tasks in Nigerian healthcare facilities, from appointment scheduling to inventory management. These systems reduce no-shows through predictive modelling and automated reminders, while also optimising staff scheduling and resource allocation.
AI-powered data aggregation tools are helping public health officials analyse surveillance data to forecast disease outbreaks and identify immunisation gaps. This enables more targeted interventions and resource allocation, improving the efficiency of public health programs.
High-Impact Future Applications for Nigeria
AI-Assisted Radiology for Rural Areas
Mobile screening units equipped with X-ray capabilities and AI analysis tools could revolutionise tuberculosis detection in rural Nigeria. These units would enable healthcare workers to conduct mass screenings in remote areas, with AI algorithms flagging potential cases for specialist follow-up.
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
AI-powered retinal image analysis could help prevent blindness by enabling early detection of diabetic retinopathy at primary care facilities. This technology would allow non-specialist healthcare workers to conduct screenings and refer patients for treatment before permanent vision loss occurs.
Maternal and Neonatal Risk Prediction
Predictive models for birth complications have shown promise in clinical trials globally. Implementing these AI systems in Nigerian hospitals could significantly reduce maternal and neonatal mortality by identifying high-risk pregnancies and enabling timely interventions.
Drug Supply Chain Optimisation
AI-driven predictive demand models could transform pharmaceutical logistics in Nigeria, reducing stockouts and wastage. These systems would analyse historical data, seasonal trends, and disease patterns to optimise inventory management and distribution.
Voice and WhatsApp-Based AI Triage Expansion
Building on the success of platforms such as AwaDoc, expanded AI triage systems could provide primary care guidance, vaccination reminders, and health education through low-bandwidth channels such as WhatsApp and voice calls. This approach would make healthcare information accessible to populations with limited internet connectivity or technological literacy.
How soon could these future applications be implemented in Nigeria?
Implementation timelines vary by application. Some technologies, such as expanded WhatsApp-based AI triage, could be scaled within 1-2 years by leveraging existing infrastructure. More complex systems, such as AI-assisted radiology in rural areas, might require 3-5 years for full implementation, depending on infrastructure development and regulatory approvals.
Benefits of AI Integration in Nigeria’s Health Sector

Improved Access
AI-powered telehealth and triage systems can significantly expand access to healthcare in remote areas. By reducing the need for in-person specialist consultations for initial assessments, these technologies lower travel barriers and bring quality healthcare to previously underserved populations.
Faster Diagnostics
AI-based imaging analysis and diagnostic support tools accelerate the detection of conditions such as tuberculosis and diabetic retinopathy. This speed enables earlier intervention, improving treatment outcomes and reducing the burden of disease.
Operational Efficiency
Administrative automation reduces workloads for healthcare staff, allowing them to focus more on patient care. AI-optimised scheduling and resource allocation improve facility efficiency and reduce waiting times.
Better Public Health Targeting
AI analytics enable more precise targeting of public health interventions, from vaccination campaigns to disease prevention programs. This precision ensures that resources are directed to where they will have the most significant impact.
Augmented Expertise
AI decision support systems extend the capabilities of healthcare workers, allowing non-specialists to provide higher-quality care. This is particularly valuable in primary care settings where access to specialists is limited.
Cost Reduction
By optimising resource allocation, reducing unnecessary referrals, and preventing disease progression through early detection, AI technologies can significantly reduce healthcare costs while improving outcomes.
Challenges and Risks in AI Healthcare Implementation
Potential Benefits
- Expanded healthcare access in remote areas
- Earlier disease detection and intervention
- More efficient resource allocation
- Reduced burden on specialists
- Improved public health planning
Implementation Challenges
- Unreliable power and limited connectivity
- Fragmented, often paper-based health records
- Shortage of AI-literate healthcare professionals
- Inadequate regulatory frameworks
- Potential for bias in AI algorithms
Infrastructure Limitations
Unreliable power supply, limited broadband connectivity, and scarce imaging hardware constrain AI deployments outside major urban centres. These infrastructure gaps must be addressed to ensure equitable access to AI-enhanced healthcare services across Nigeria.
Data Quality and Availability
AI systems require high-quality, labelled data for training and operation. Nigeria’s health records are often fragmented or paper-based, creating challenges for data collection and standardisation. Efforts to digitise health records and establish data standards are essential for effective AI implementation.
Skill and Capacity Shortages

Many healthcare professionals in Nigeria lack the digital literacy needed to use AI tools effectively. Training programs for clinicians, technicians, and health managers are crucial to building the capacity required for successful AI integration in healthcare settings.
Regulatory and Legal Gaps
Nigeria currently lacks a comprehensive regulatory framework specific to AI in healthcare. While the Nigeria Data Protection Regulation (NDPR) provides some foundation, it does not fully address the unique challenges of algorithmic governance and clinical validation for AI health technologies.
Bias, Safety, and Clinical Validation
AI models trained on non-representative data may perform poorly for Nigerian populations, potentially leading to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment recommendations. Rigorous clinical validation with diverse local populations is essential to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Cybersecurity and Privacy Concerns
The sensitive nature of health data requires robust protection against breaches and misuse. As healthcare systems become more digitised and interconnected, strengthening cybersecurity measures is increasingly essential for maintaining patient trust and data integrity.
Regulatory Framework for AI in Nigeria’s Health Sector
WHO Guiding Principles for AI in Health
The World Health Organisation has established six guiding principles for AI in healthcare: protecting autonomy, promoting human well-being and safety, ensuring transparency, fostering accountability, ensuring inclusiveness and equity, and promoting responsive and sustainable AI. These principles provide a valuable framework for Nigeria’s regulatory approach.
Current Regulatory Landscape in Nigeria
Nigeria’s existing data protection regulation (NDPR) provides some foundation for AI governance but lacks specific provisions for healthcare applications. The National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA) and the National Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (NCAIR) are developing more comprehensive frameworks for AI regulation.
The absence of sector-specific AI regulations creates uncertainty for developers and healthcare providers, potentially slowing innovation and adoption. A clear regulatory pathway is needed to ensure that AI healthcare solutions meet appropriate standards for safety, efficacy, and ethical use.
| Regulatory Aspect | Current Status | Recommended Development |
| Data Protection | Covered by NDPR but lacks healthcare specificity | Healthcare-specific data protection guidelines |
| Clinical Validation | No formal requirements | Standardised validation protocols for AI health tools |
| Risk Classification | Not established for AI health tools | Risk-based regulatory framework |
| Liability Framework | Unclear for AI-assisted decisions | Clear liability guidelines for AI use in healthcare |
| Certification Process | No formal process for AI health tools | Streamlined certification pathway |
Stay updated on AI Analysis and trends in Nigeria.
Join our newsletter to receive the latest updates, news and analysis like this.
Policy Recommendations for Effective AI Integration
Adopt a Health-Sector AI Framework
Nigeria should develop a comprehensive regulatory framework for AI in healthcare, grounded in WHO principles. This framework should establish risk classes for different AI applications, with higher evidence requirements for higher-risk tools. A phased implementation approach would allow for adaptation and refinement based on real-world experience.
Align Legal and Data Protection Standards
The Nigerian Data Protection Regulation should be aligned with AI governance requirements for healthcare. This includes establishing clear rules for patient consent, data minimisation, and cross-border data flows. Health-specific AI regulations should address the unique challenges of medical data and clinical applications.
Establish Clinical Validation Requirements

Nigeria should introduce certification or approval pathways for AI tools intended for clinical use. These pathways should require independent clinical trials or local validation studies before routine deployment. Regulatory sandboxes can provide controlled environments for piloting new technologies before wider implementation.
Invest in Infrastructure and Local Data
Expanding reliable power and broadband connectivity in regional hospitals is essential for the adoption of AI. Efforts to digitise medical records and establish secure, de-identified health datasets will improve model training and ensure AI tools are fair and effective for Nigerian populations.
Build Local Capacity
Training programs for clinicians, data scientists, and ethics committee members are needed to build the human capacity required for effective AI implementation. Integrating AI literacy into medical curricula and continuing professional development will ensure healthcare professionals can effectively use and evaluate AI tools.
Implement Cybersecurity and Privacy Safeguards
Minimum security standards should be mandated for systems that store or process health data. Breach notification requirements and penalties for negligence will help protect patient data and maintain trust in digital health systems.
Support Local Innovation
Public procurement processes should support the development of locally developed AI solutions tailored to the Nigerian context. Public-private partnerships can accelerate innovation and ensure that AI technologies address the specific needs and challenges of Nigeria’s healthcare system.
Conclusion
A Balanced Approach to AI in Healthcare
AI has the potential to significantly transform Nigeria’s health sector, expanding access to quality healthcare, improving diagnostic accuracy, and optimising resource allocation. The country’s early implementations, such as AwaDoc’s WhatsApp chatbot and various telemedicine platforms, demonstrate the feasibility and impact of AI-enhanced healthcare services.
However, realising the full potential of AI in healthcare requires addressing significant challenges related to infrastructure, data quality, skills, regulation, and ethical considerations. A balanced approach that prioritises patient safety, equity, and clinical validation is essential for the responsible adoption of AI.
With deliberate investment in infrastructure and capacity building, clear regulatory frameworks, and support for local innovation, Nigeria can move from promising pilots to the scaled, sustainable implementation of AI. The result will be a stronger, more accessible healthcare system that better serves all Nigerians.

Senior Reporter/Editor
Bio: Ugochukwu is a freelance journalist and Editor at AIbase.ng, with a strong professional focus on investigative reporting. He holds a degree in Mass Communication and brings extensive experience in news gathering, reporting, and editorial writing. With over a decade of active engagement across diverse news outlets, he contributes in-depth analytical, practical, and expository articles exploring artificial intelligence and its real-world impact. His seasoned newsroom experience and well-established information networks provide AIbase.ng with credible, timely, and high-quality coverage of emerging AI developments.

