Understanding AI-Powered EdTech Learning Platforms
AI-powered EdTech learning platforms combine artificial intelligence technologies with educational content to create dynamic, responsive learning environments. Unlike traditional e-learning systems, these platforms continuously adapt to each student’s performance, learning pace, and preferences.
In the Nigerian context, these platforms are designed to address specific local challenges, including language diversity, curriculum alignment with national standards, and infrastructure limitations. They leverage machine learning algorithms to analyse student interactions, identify knowledge gaps, and automatically adjust content difficulty.
The core components of an AI-powered EdTech platform in Nigeria typically include:
- Personalised learning paths that adapt based on student performance
- Content libraries aligned with the Nigerian educational curriculum
- Interactive assessments with real-time feedback
- Progress tracking and analytics for students, parents, and teachers
- Multilingual support for Nigeria’s diverse language landscape
- Offline functionality to address connectivity challenges
Market Opportunity in Nigeria
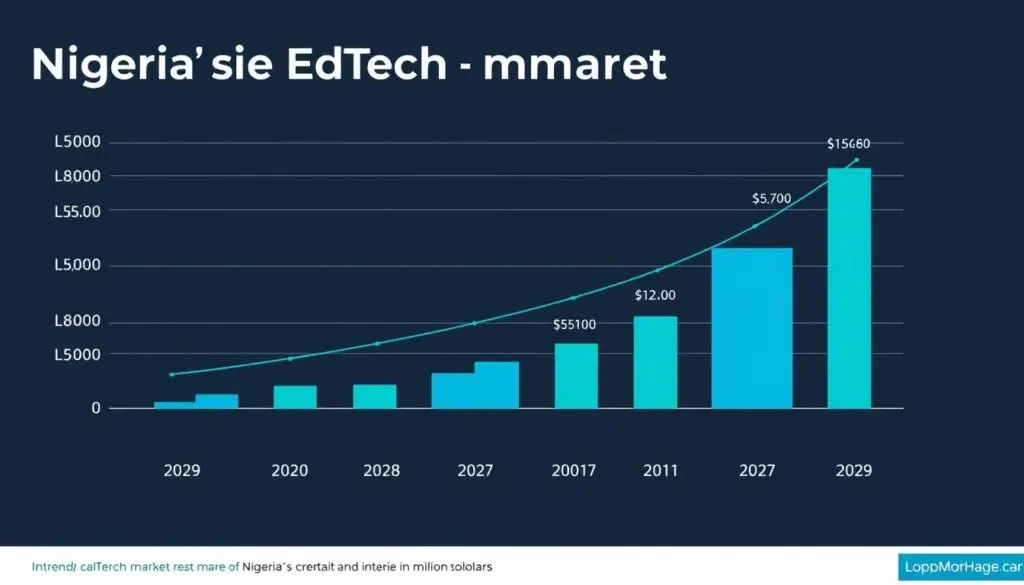
Nigeria’s EdTech market presents a substantial opportunity for AI-powered learning platforms. With Africa’s largest population and over 65% under the age of 25, the country has an enormous student base seeking quality education. The Nigerian EdTech market is currently valued at approximately $400 million and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 16% through 2027.
Primary & Secondary Education
With millions of students enrolled, this segment represents the most significant market opportunity. Parents increasingly seek supplementary learning tools to help their children excel in a competitive educational environment.
Tertiary Education
Nigeria’s 170+ universities and polytechnics face capacity challenges. AI platforms can help scale quality education to the 2+ million tertiary students seeking specialised knowledge and skills development.
Professional Development
Working professionals seeking to upskill represent a growing market segment. AI-powered platforms can deliver targeted training aligned with industry needs and workplace requirements.
“The edtech market in Nigeria is valued at $400 million, a 48% jump from its value in 2024. This rapid growth signals strong demand for innovative educational solutions.”
Technical Implementation of AI in Nigerian EdTech
Building an effective AI-powered EdTech platform for Nigeria requires sophisticated technical implementation tailored to local needs. The core AI technologies driving these platforms include machine learning for personalisation, natural language processing for content adaptation, and data analytics for tracking progress.
Key AI Components
Personalised Learning Paths
Machine learning algorithms analyse each student’s performance data, identifying strengths, weaknesses, and learning patterns. The system then creates customised learning paths that adapt in real-time as the student progresses.
Content Adaptation
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables platforms to present content in different formats and complexity levels based on student needs. For Nigerian students, this includes adapting materials to different English proficiency levels and local contexts.
Intelligent Assessment
AI-powered assessment tools go beyond multiple-choice questions to evaluate deeper understanding. These systems can analyse written responses, project work, and even practical demonstrations to provide comprehensive feedback.
Predictive Analytics
By analysing patterns across thousands of students, these platforms can predict learning outcomes and identify students at risk of falling behind, enabling early intervention by teachers or the system itself.

Local Innovation Spotlight: Cubbes, a Lagos-based AI-powered EdTech platform, has developed a system that combines AI-driven study tools with peer mentorship networks. Their platform has helped students achieve average grade improvements of over 50%, and 80% of first-class graduates at the University of Lagos attribute their success to it.
Sustainable Revenue Models
Successful AI-powered EdTech platforms in Nigeria implement multi-tiered revenue models that balance affordability with sustainability. These approaches recognise the diverse economic realities across Nigerian society.
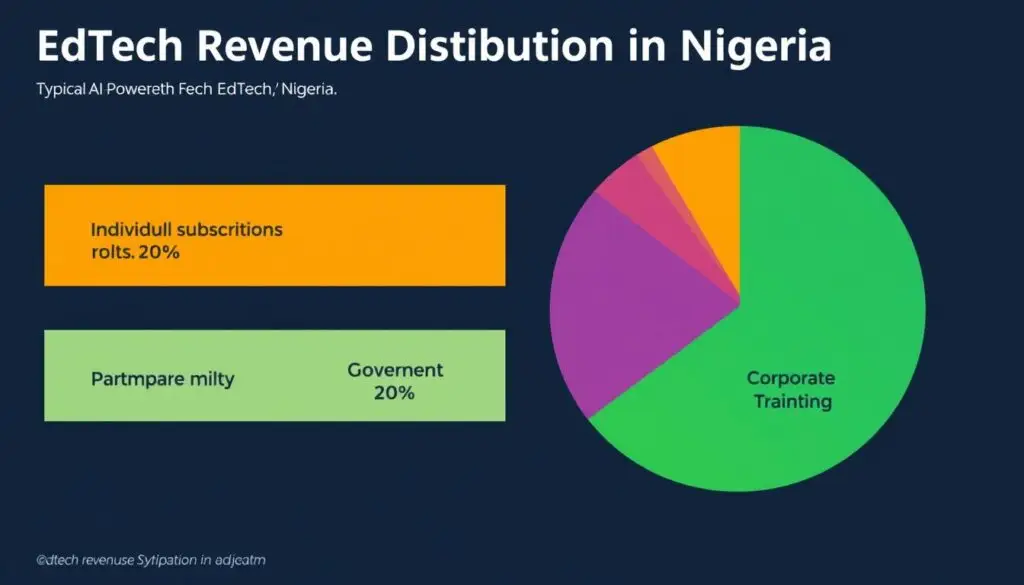
| Revenue Stream | Target Segment | Pricing Strategy | Value Proposition |
| Individual Subscriptions | Students & Parents | Freemium with tiered pricing (₦1,500-5,000/month) | Personalised learning, improved academic performance |
| School Partnerships | Private & Public Schools | Per-student licensing (₦800-2,000/student/year) | Enhanced teaching tools, improved outcomes, and analytics |
| Government Contracts | State & Federal Education Agencies | Large-scale deployment contracts | Scalable quality education, standardised assessment |
| Corporate Training | Businesses & Organizations | Enterprise licensing & custom solutions | Workforce development, specialised training |
Successful platforms often start with a freemium model to build a user base, then expand into institutional partnerships. For example, Breni, a Nigerian AI learning app, offers a free version with ads while charging premium subscriptions ranging from $1 in Nigeria to $5 internationally, adjusting pricing to local economic conditions.
Implementation Challenges in Nigeria
Despite the enormous potential, implementing AI-powered EdTech platforms in Nigeria faces several significant challenges that must be addressed for successful adoption and impact.
Opportunities
- Large, young population eager for quality education
- Growing smartphone penetration (over 40%)
- Government initiatives supporting educational technology
- Rising private investment in EdTech startups
- Increasing awareness of AI benefits in education
Challenges
- Inconsistent internet connectivity, especially in rural areas
- Limited digital literacy among teachers and some students
- Cost barriers for many potential users
- Power supply instability is affecting device usage
- Curriculum alignment with national education standards

Addressing the Challenges
Connectivity Solutions
Successful platforms implement offline functionality, content caching, and low-bandwidth optimisation. Some partners with telecom providers to offer zero-rated access, allowing students to use educational platforms without data charges.
Localization Strategies
Effective platforms adapt content to Nigerian curriculum standards, cultural contexts, and learning styles. This includes supporting multiple languages and incorporating locally relevant examples and case studies.
Accessibility Approaches
To overcome economic barriers, platforms implement tiered pricing, institutional partnerships, and cross-subsidisation models where premium users help fund access for underserved communities.
“Building in Africa is already tough, but building in Nigeria is even tougher. There’s a mindset gap when it comes to startups and technology adoption.”
Critical Success Factors
For AI-powered EdTech platforms to succeed in Nigeria’s unique environment, several key factors must be prioritised in their design and implementation.
Mobile-First Design
With smartphone penetration exceeding PC access in Nigeria, successful platforms prioritise mobile experiences. This means lightweight applications optimised for Android devices, responsive interfaces, and touch-friendly interactions.
Example: Cubbes built a mobile-first platform with lightweight applications optimised for low-data use and incorporated offline-first features so students can access resources without constant connectivity.
Cultural Relevance
Platforms that incorporate Nigerian contexts, examples, and scenarios in learning materials see higher engagement and retention. This includes supporting local languages and adapting content to reflect familiar situations.
Example: Breni offers content in multiple languages, including Hausa, enabling students in Northern Nigeria to learn in their preferred language and addressing a key barrier to educational access.
Teacher Integration
Rather than replacing teachers, successful platforms augment their capabilities with AI-powered tools for assessment, content creation, and student monitoring.
Example: DLN’s $1 billion project includes comprehensive teacher training programs to ensure educators can effectively integrate AI tools into their teaching practice.

Future Outlook and Impact
The trajectory of AI-powered EdTech platforms in Nigeria points toward a transformative impact on the country’s educational landscape. As these technologies mature and adoption increases, several key developments are likely to emerge.

Emerging Trends
AI-Human Collaboration
The future will see deeper integration between AI systems and human educators, with AI handling personalisation and assessment while teachers focus on mentorship, creativity, and social-emotional learning.
Cross-Border Learning
Nigerian AI-powered platforms are already finding unexpected success in international markets. Breni, for example, has 90% of its users outside Nigeria, with significant adoption in Nepal, Russia, and other countries.
Workforce Alignment
Future platforms will increasingly bridge education with employability, using AI to align learning outcomes with job-market demands and to provide credentials recognised by employers.
Data-Driven Policy
The rich data generated by these platforms will inform evidence-based education policy, helping government and institutions make more effective decisions about curriculum, resource allocation, and interventions.
SDG Impact: AI-powered EdTech platforms directly contribute to UN Sustainable Development Goal 4 (Quality Education) by expanding access to personalised, quality learning opportunities. By 2030, these technologies could help Nigeria make significant progress toward universal completion of secondary education and improved learning outcomes.
Transforming Nigeria’s Educational Future
AI-powered EdTech learning platforms represent a significant opportunity to address Nigeria’s educational challenges at scale. By combining the power of artificial intelligence with thoughtful localisation and sustainable business models, these platforms can democratize access to quality, personalised education across the country.
The success stories of platforms like Cubbes, Breni, and initiatives like the NAPPS-DLN partnership demonstrate that AI-powered education is not just a future possibility but a present reality in Nigeria. As these technologies continue to evolve and adapt to local needs, they have the potential to transform not just how students learn, but the entire educational ecosystem—empowering teachers, informing policy, and creating pathways to economic opportunity.
For Nigeria to fully realise this potential, continued collaboration between technologists, educators, investors, and policymakers will be essential. The journey toward AI-enhanced education has begun, and its promise for Nigeria’s 65 million students is profound.

Senior Reporter/Editor
Bio: Ugochukwu is a freelance journalist and Editor at AIbase.ng, with a strong professional focus on investigative reporting. He holds a degree in Mass Communication and brings extensive experience in news gathering, reporting, and editorial writing. With over a decade of active engagement across diverse news outlets, he contributes in-depth analytical, practical, and expository articles exploring artificial intelligence and its real-world impact. His seasoned newsroom experience and well-established information networks provide AIbase.ng with credible, timely, and high-quality coverage of emerging AI developments.

